1= CHRONAXIA. It is the duration of shortest impulse that will produce a response with current of double the rheobase. • At the double Intensity of rheobase,the minimal pulse width required to produce the twitch is called chronaxie of muscles. • chronaxie is sn index of excitability and is time in millisecond, necessary to induce minimal visible contraction with a stimulus of twice the strength of rheobase. • Normal value of chronaxie are less than ( 0.05 to 0.5) • variation in chronaxie depending on wheather a constant current machine or a constant voltage machine is used. • At birth chronaxie is 10 times higher than normal and 18 to 20 th month, the chronaxie falls to normal value. FACTOR RESPONSIBLE FOR CHRONAXIE. •Texture of skin • lschemia. • Fatigue. •position of stimulating electrodes. • Denervation. • Nerve root lesion.
2= RHEOBASE. It is smallest current that produce muscle contraction if stimulus is on infinite duration. *Mainly 100 to 300 ms duration are used to record rheobase. *The pulse is always rectangular measured in milliamperes or volts. * Rheobase is measured using the cathode on the motor piont of thr nerve or by using bipolar technique. * Normal value of rhrobase are 2 to 18 mA or 5 to 35 volts. FACTOR RESPONSIBLE FOR RHEOBASE. •Resistance of skin and subcutaneous tissue. • Edema and inflammation. • Temperature variation. • position of electrodes. • Degeneration. • Denervation.
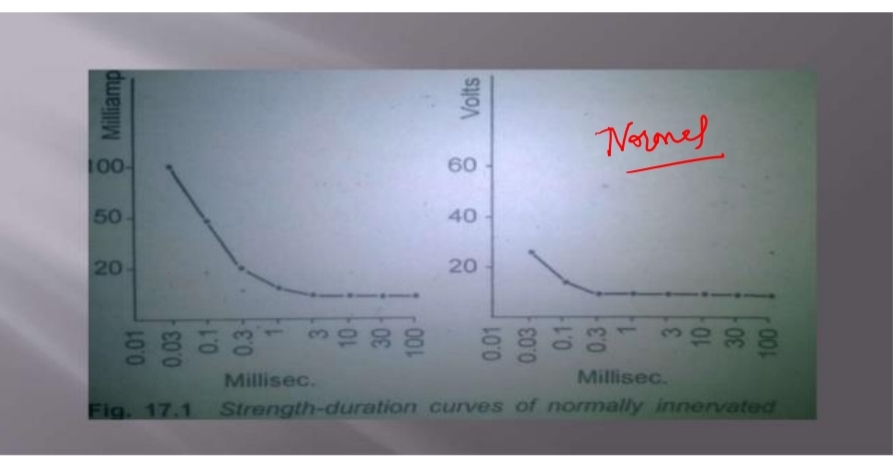
3= SD CURVE. Strength duration graph is useful for finding the muscle where Innervated and where denervated. SD GRAPH.

4= PULSE RATIO. It is the ratio of the intensity of the current needed to produce a muscle contraction with 1msec duration to that intensity at 100ms.
•If the ratio is = less than 2.2,it is the case of Innervation. • 2.2 to 2.5, it is partial innervation. • 2.5, it is denervation.
5= NERVE EXCITIBILITY TEST. We give it for 2 purposes:. a) To see excitibility of muscle. b) to see conduction of nerve. A rectangular pulse is given an normal side first for 1ms or 0.1 msec and on the affected side. • The minimum current is required to produce contraction at this particular duration is noted for both normal and affected side. The difference b/w the two is then noted. • If the difference is b/w 0 to 2 mA= either muscle is normal or there is neuropyraxia. • b/w 3 to 8 mA = so,there is immediate axontemesis or old neuropyraxia. • 8 mA= old neurotemesis or neuropyraxia.
6= FG TEST. •The point of maximum stimulation shifts downwards. • polar reaction serves or absence in case of denervation ( i.e, pleuger’s law is not followed,i.e response will be better fr anode then cathode or both will give equal response.
REACTION OF INNERVATION HAS FOLLOWING CHARACTERISTICS:_ • Response to faradic current is present. • Response to galvanic stimulation is fast. • point of maximum stimulation shift upwards. • polar reaction is present ( muscle follows pleugers’s law.) • The reaction of accomodation to a slow rising current like Traingular pulse will be present.
REACTION OF DENERVATION HAS FOLLOWING CHARACTERISTICS. •Response to the faradic current is absent. • Response to the galvanic stimulation is slow. • Point of maximum stimulation shift downward. • polar reaction reverse or absense in case of denervation( i.e pleugers’s law is not followed i.e response will be better from anode and cathode or both will be equal response. •high intensity of current is required in case of denervation as compared to normal side. • The reaction of accomodation to a slow rising current like Traingular pulse will be absent in case of denervation (i.e) accomodation is a phenomenon of nerve,nerve is affected, there will no accomodation and contraction will remain same thoughout.
Nyce
LikeLiked by 1 person
Keep it up 👌
LikeLiked by 1 person
Great way for giving knowledge its too good 👌👌👌and helpful
LikeLiked by 1 person
Niceee
LikeLiked by 1 person
Very helpful👍
LikeLiked by 1 person
Keep going 🤗
LikeLiked by 1 person
Well done👍
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanku ☺️
LikeLike