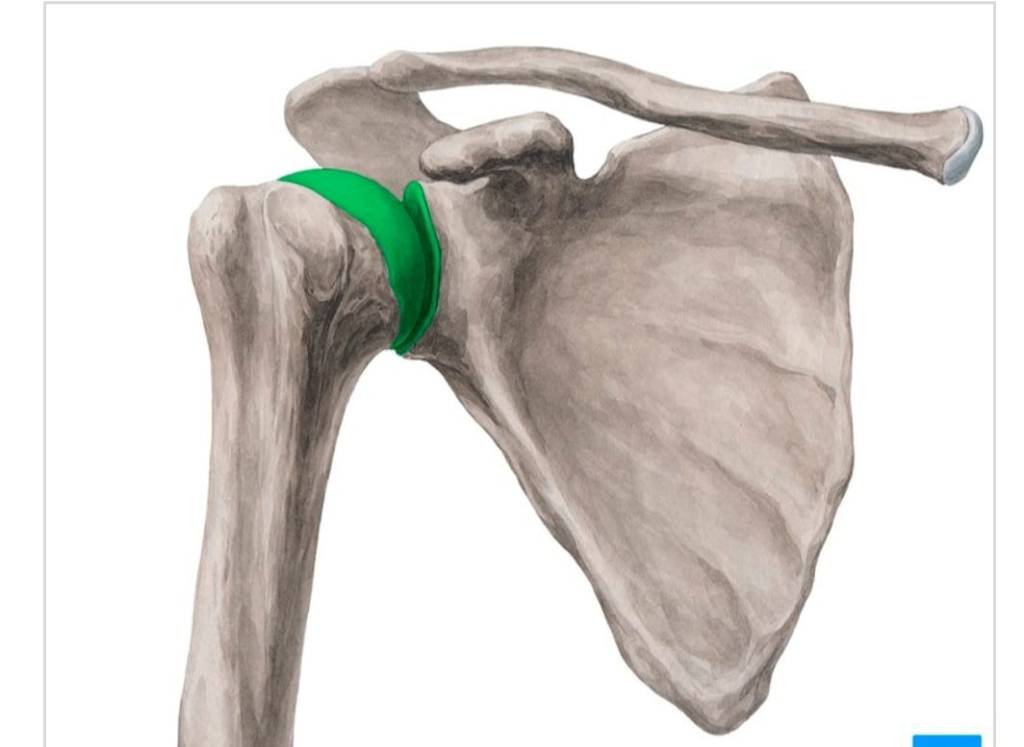
Features= synovial joint= Ball and socket joint between the scapula and humerus.it has greater mobility than any other joint in the body.
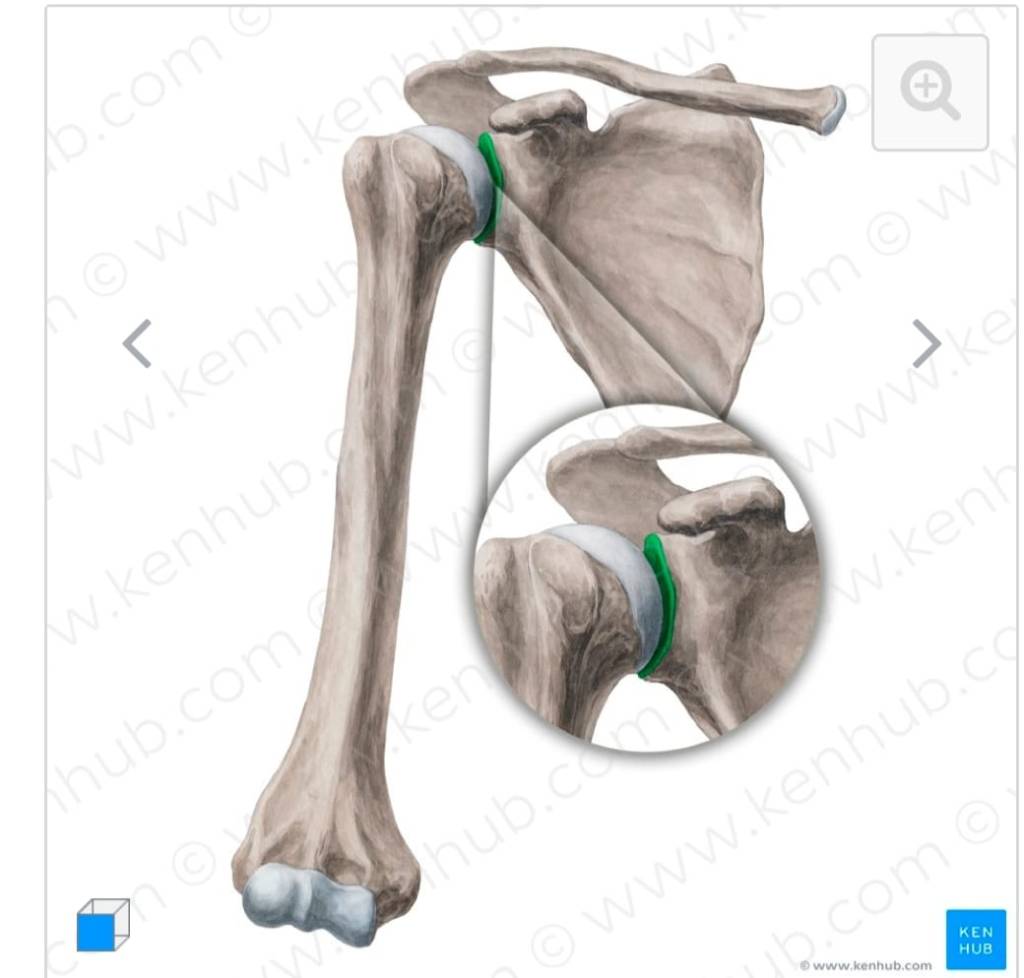
Articular surface= Gleniod fossa of scapula,head of humerus; gleniod labrum. Ligaments. 1.Capsular ligament. ( Superior,middle and inferior) 2.Coracohumeral ligament. 3.Transverse and humeral ligament. Muscles actiong on the shoulder join= The scapulohumeral and thoracohumeral muscles. Movements at synovial joint. 1.Flexion(110°) 2.Extension(60°) 3.Adduction(0°) 4.Abduction(120°) 5.Pronation(70°) 6.Supination(85°) 7.Circumduction. 8.Rotation 9.Inversion. 10.Eversion.
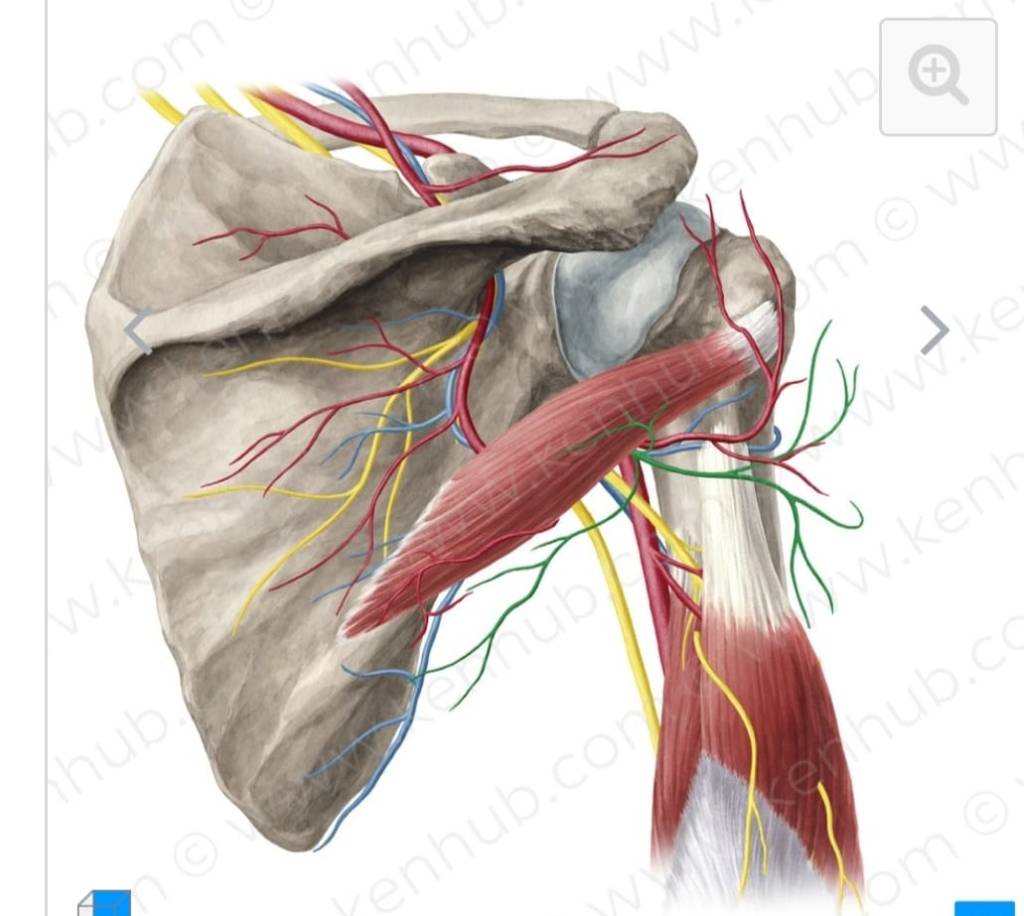
Blood supply of the shoulder joint. ACHA= Anterior circumflex humeral arteries. PCHA=posterior circumflex humeral arteries Innervation= is provided by the axillary suprascapular and lateral pectoral nerves.
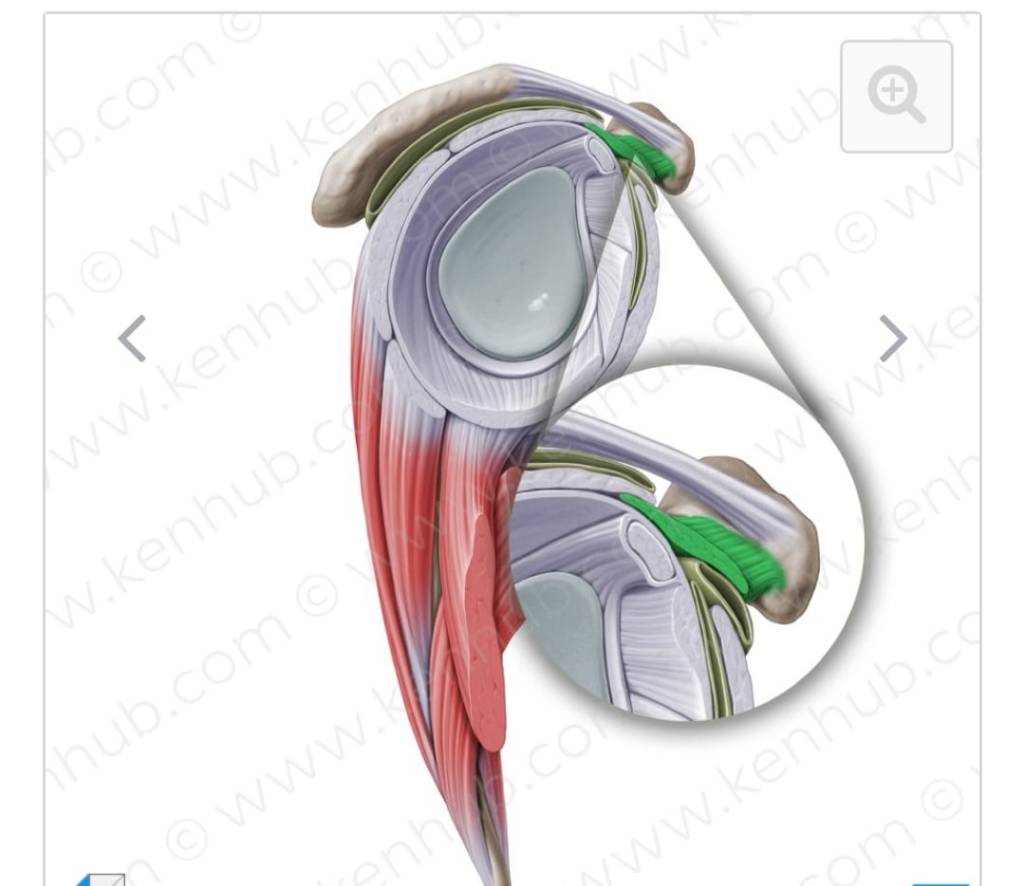
Shoulder pain and exercises. Rotator cuff injury is most common cause of shoulder pain.work of these muscles is dynamic stable of the shoulder.supraspinatus tendonitis is commonest of all four rotator cuff muscles( supraspinatus,infraspinatus,teresminor and subscapularis).
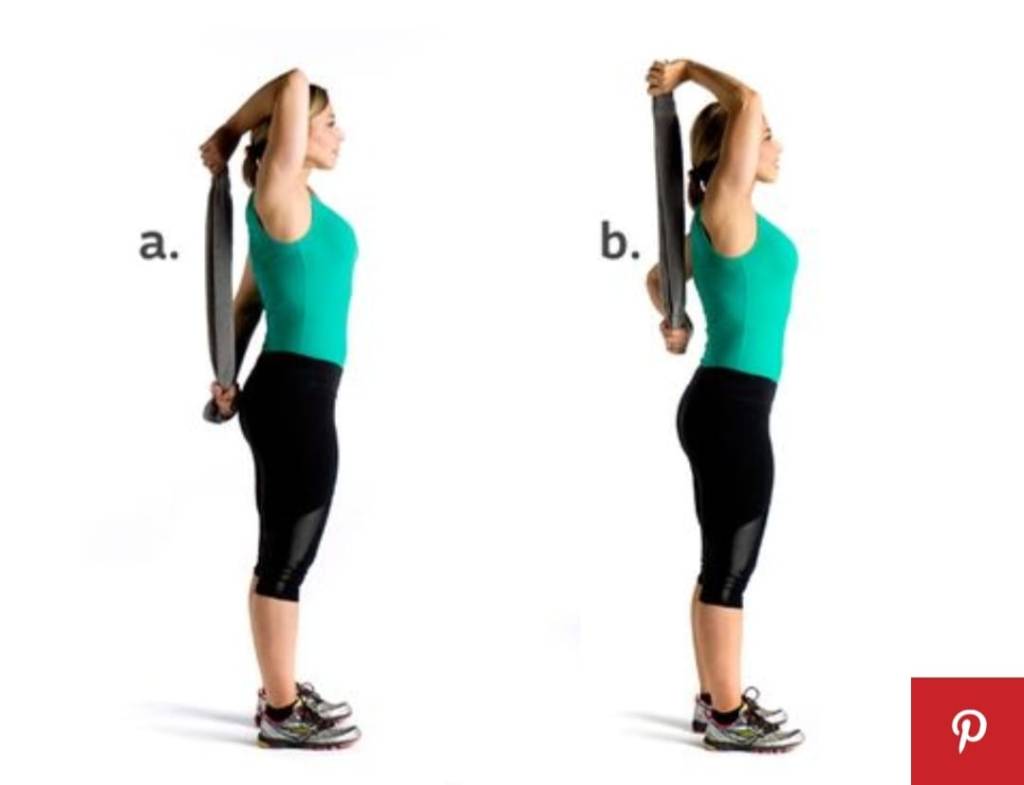
Rotator cuff strengthening exercises are:-
1.internal rotation exercises=roll up a towel and with the hand that you’re not going to stretch with put it up and behind you then the one you want to stretch is going to go down.
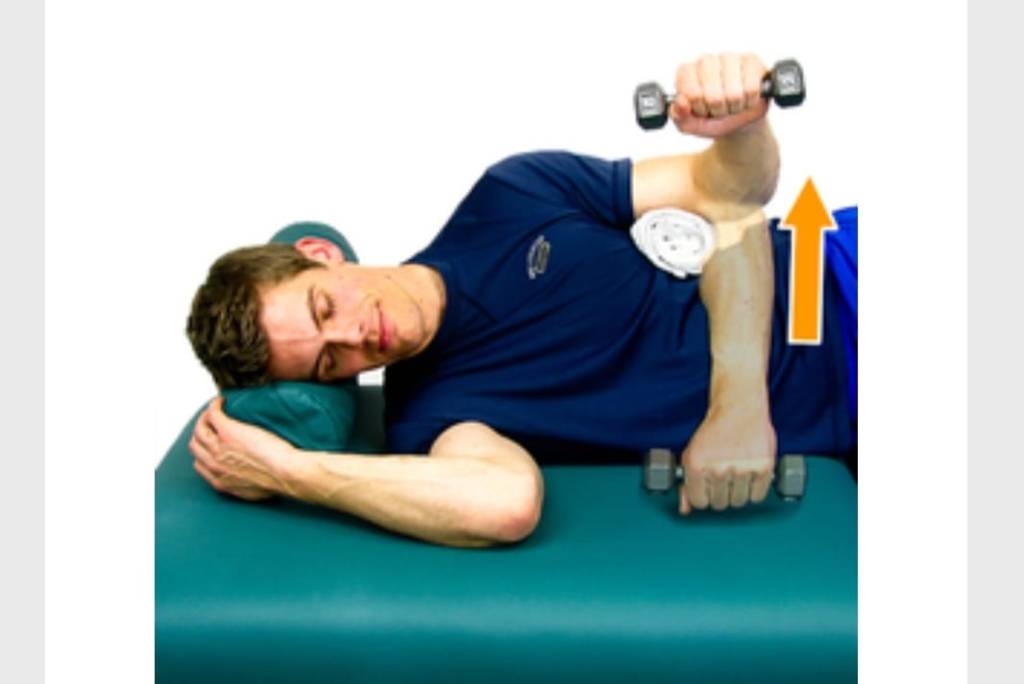
2.External rotation in side lying position with weight cuff=weight in hand.a slowly twist your arm and raising your hand toward the sky,without moving your elbow. Do this for 5- to 10 reps and repeat 3 times.
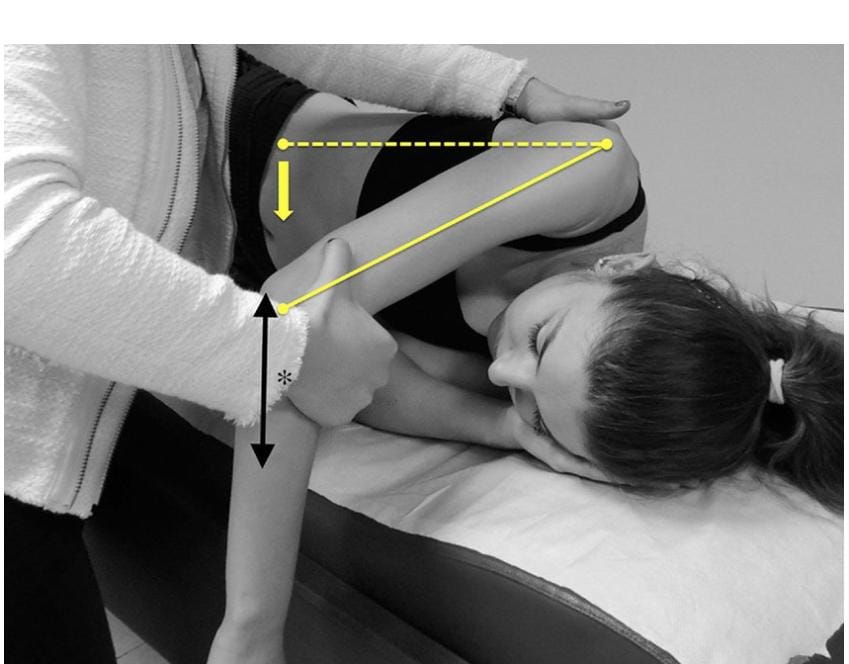
3. Posterior capsule stretch for shoulder to increase shoulder flexibility= A posterior capsule stretch is a good stretch to help with shoulder impingement and rotator cuff issue. •take the arm you want to stretch and bring it across your body at shoulder height with your plam down. •Take your other hand and push your arm at your elbow further across your body until you feel a stretch, and hold it.