Mobilization:
They are passive skilled manual therapy techniques
applied to joints and related soft tissues
at varying speeds and amplitudes using
physiological or accessory motions for
therapeutic purposes.
speeds and amplitudes could range from
small-amplitude force applied at high
velocity
to a large-amplitude force applied at slow
velocity
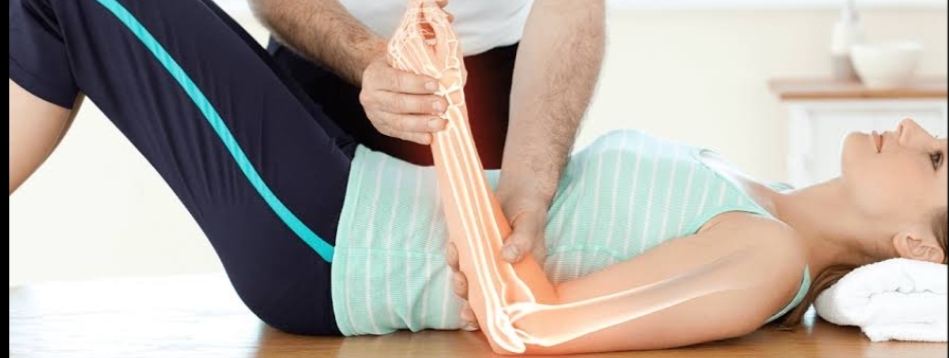
Joint mobilization
Joint mobilization refers to manual therapy techniques used
to modulate pain and
treat joint dysfunctions
regain range of motion (ROM)
addressing the altered mechanics of the
joint.
The altered joint mechanics may be
due to
- pain
- muscle guarding
- joint effusion
- Contractures
- adhesions in the joint capsules
- Adhesions in supporting ligaments
- Malalignment.
- Subluxation of the bony surface.
Mobilization with Movement
Mobilization with movement (MWM) is
accessory mobilization applied by the
therapist
an active physiological movement to end
range applied by the patient
The technique is always applied in
a pain free direction
describe as correcting joint tracking
from positional fault
Manipulation
Manipulation refer to :
a high-velocity thrust of small
amplitude performed at the limit of
available movement

Manipulation Under Anesthesia
Manipulation Under Anesthesia
is a medical procedure
used to restore full ROM
by breaking adhesions around a joint
while the patient is anesthetized.
The technique may be a rapid thrust or a passive stretch
using physiological or accessory movements
Muscle Energy Technique:
Muscle energy technique:
active contraction of deep muscles that attach near the joint whose line of pull can cause the desired accessory motion.
The therapist stabilize the segment on which the distal aspect of the muscle attaches.
Physiological movements are the movements that patient can do voluntarily.
e.g., the classic or traditional movement such as flexion and
abduction, rotation.
term osteokinematics is used for these Accessory Movements.
Accessory movements are the movements in the joint and
surrounding tissue
that are necessary for normal ROM
cannot be actively performed by the patient
Terms related to accessories movements are. •components motion. •joints play.
