Neuroanatomy is the study of nervous system.The nervous system is the most complex and widely investigate d and least understood system in the body. *Nervous system is also called master system of the body.
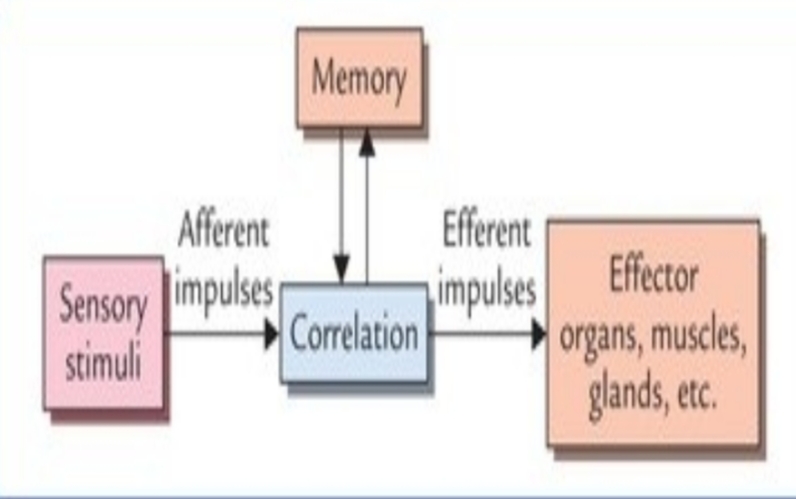
Function of nervous system includes:_. 1) Reception of sensory stimuli from internal to external environment. 2) coordination and control of voluntary action the body. 3) Assimilation of experiences, learning,memory and intelligency. 4)Integration of sensory information.
Nervous system consists of three functional types of neurons. • sensory= The sensory neuron detect stimuli and motor neurons send commands to the effector organ •motor. •Interneurons=capacity to analyze, integrate and store information.
Mechanisms of nervous system.
Division of nervous system. •Anatomical= Divided into two parts central nervous system(CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). 1)CNS=consists of brain and spinal cord.The CNS is responsible for integrating,processing and coordinating sensory data and giving motor commands.it is responsible for memory, learning and emotions and intelligence. 2)PNS= includes all neural tissues outside the CNS such as 12 pair of cranial nerve, and 31 pair of spinal nerve and ganglia associated with cranial and spinal nerve.The PNS provide sensory information to the CNS and carries its motor command to the peripheral tissues and system.
•Functional= Functionally also the nervous system it divided into two parts. 1)The afferent division= Bring sensory information to the CNS. 2) The efferent division= carries motor commands to the muscles and glands.
NEURONS. A neurons also known as( neurone and nerve cell)is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signal.neurons are core components of the nervous system, which includes brain,spinal cord and peripheral ganglia.
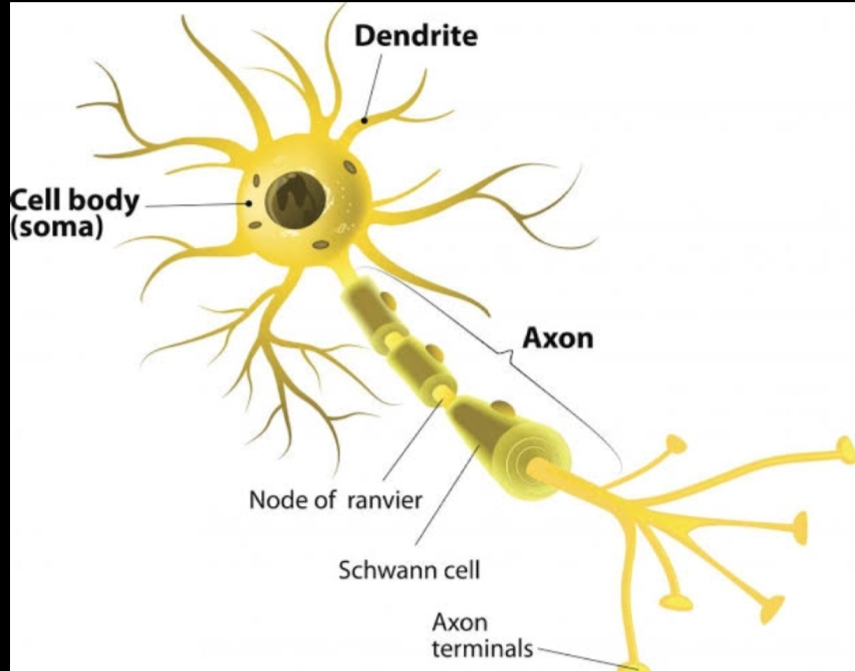
STRUCTURE OF NEURONS. A neurons consist of three main parts:_the cell body ( soma) dendrites and axons. The cell body is the central region which is the most important parts of the neuron containing the necleus of the cell. • neurons receive signals via the dendrite and send outside signals down the axon.
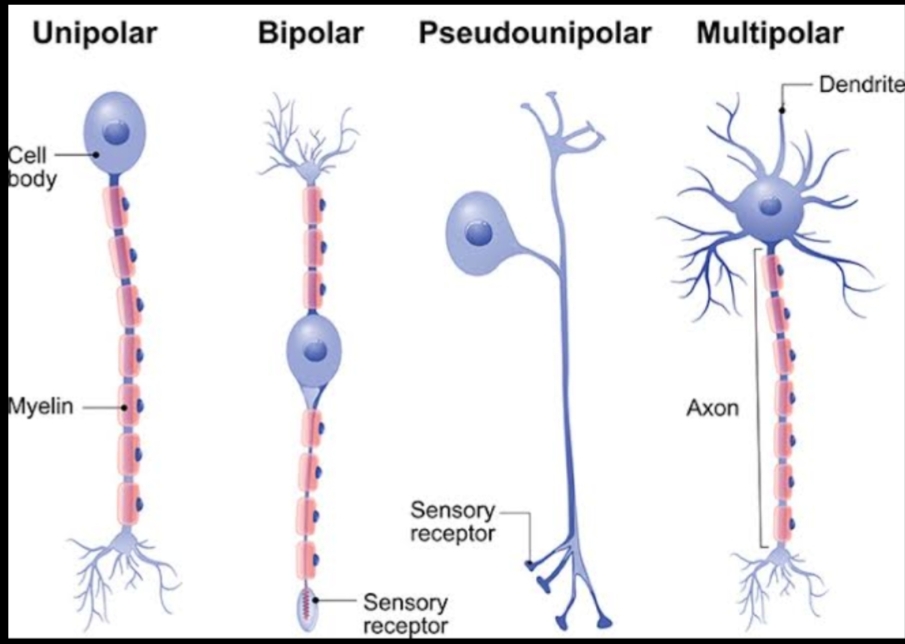
CLASSIFICATION OF NEURONS. *BASED ON POLARITY. Unipolar=types of neuron in which only one protoplasmic process( neurite) extend from the cell body= In human mostly found in dorsal root ganglia. Pseudounipolar= contains an exon that has splits into two branches, one branch runs to the periphery and other run to the spinal cord. Bipolar=An exon and a single dendrite on opposite ends of the soma_ are specialized sensory neuron of the transmission of special senses, hence abundant in sensory pathways for smell and sight,taste hearing and vestibular. multipolar=An axon along with more than two dendrite= multipolar neurons constitute the majority of neurons in the brain_subdivided in to golgi I and II gogli type_ includes motor neuron and interneurons
FUNCTIONAL CLASSIFICATION. • sensory neurons=They carry impulse from the receptor organ to the CNS. Primary sensory neurons=The cell bodies of these neurons lie outside the CNS( except those of mesencephalic nucleus of fifth cranial nerve which lie within the CNS) secondary sensory neurons =The cell bodies of these neurons lie in the CNS. Tertiary sensory neuron=The cell bodies of these neurons lies in the thalamus.
*MOTOR NEURONS Types of motor neuron. In the somatic nervous system they are divided into two parts. 1) Upper motor neuron=Have their cell bodies located in the cerebral hemisphere,i.e motor area of the cerebral cortex. They form the descending pathways of the brain and synapse with the motor neurons Of the cranial nerve nuclei in the brainstem and motor neurons of the spinal nerve in the anterior horns of the spinal cord. The upper motor neurons are involved in the voluntary control of muscular activity. Lower motor neurons= have their cell bodies located in the brainstem and spinal cord. • The skeletal muscles are supplied by the motor neurons of the anterior horn in the spinal cord and in the motor neuclei of cranial nerve. These neurons from the final common pathway for determining the muscle action and are collectively known as lower motor neurons.
NEUROGLIA.
• The neuroglia are the interstitial or supporting
cells of the nervous system. They do not
contribute to the propagation of impulses or the
processing of the perceived information but
support the neurons both structurally and
functionally.
• Neuroglia in the central nervous system
• There are four main types of neuroglia (glial cells)
in the CNS: (a) astrocytes, (b) ependymal cells,
(c )oligodendrocytes, and (d) microglia
• Astrocytes are the largest and most numerous, and form the main
supporting tissue of the nervous system. They are star-shaped as the
name implies and possess many fine dendrite-like processes. At the ends
of processes there are small swellings called foot-processes.
•Ependymal cells line the ventricles of the brain and
central canal of the spinal cord. Ependymal cells
are of three types: (a) ependymocytes, (b) choroid
epithelial cells, and (c) tanycytes.
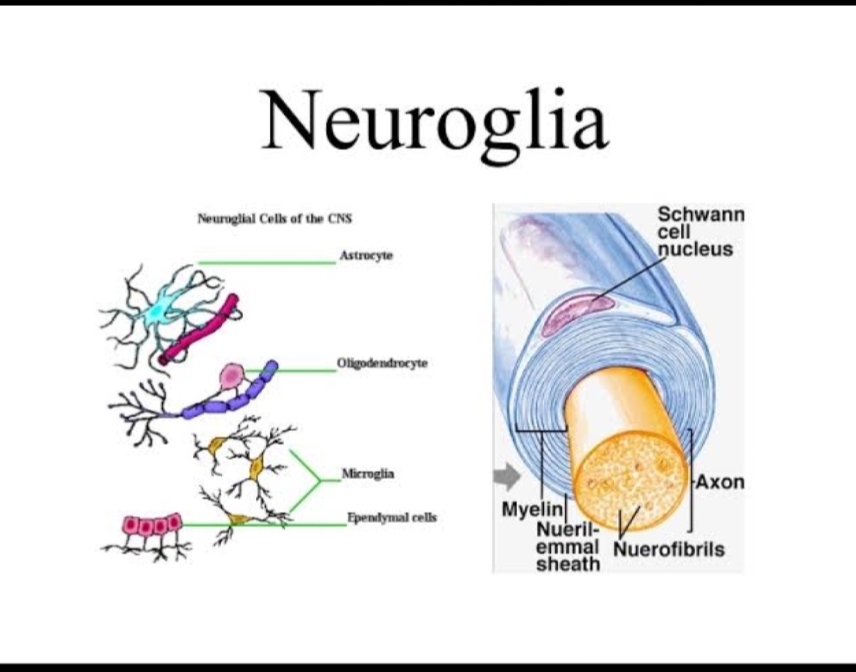
• Oligodendrocytes are smaller than astrocytes
and as the name implies have fewer
processes. They are found (a) in clusters
around the neurons of grey matter, and (b)
adjacent to and along the length of
myelinated nerve fibres in the white matter
•
– Microglias are the smallest of the glial cells, and are
capable of migrating through the surrounding neural
tissue. Microglia do not develop in the neural tissue.
They are derived from phagocytic white blood cells
(fetal monocytes) that migrate from the blood into the
nervous system before birth.
• The microglia enlarges and become phagocytic in
areas of inflammation and cell destruction. They
remove cell debris, wastes and pathogens that
invade the CNS by phagocytosis.

Keep it up 👍
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanku 💕
LikeLike
Nyc … 🔥
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanku 😊
LikeLike