Definition
Massage is the scientific manipulation of soft tissues of the
body with the palmar aspect of hands(s) and or fingers.
Massage is a tern applied to certain manipulation of the soft
tissues.
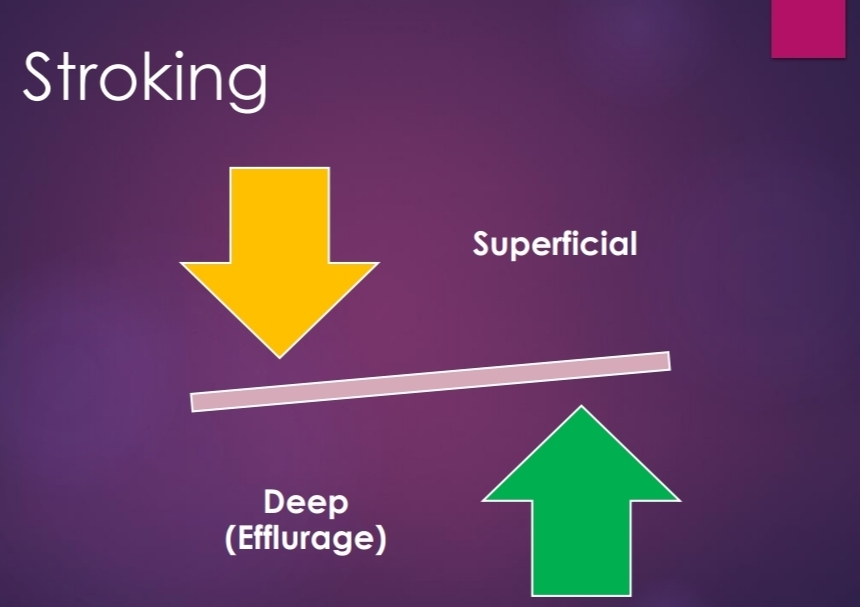
Superficial stroking
the rhythmic movement of hand or parts of hand, over
the skin the lightest amount of pressure in order to
obtain sensory stimulation.
Strokes can be applied from proximal to distal part or
vice versa. (Centrifugal of Centripetal) .
Every massage should begin and end with strokes.
It can also be used between every other technique.
It is best performed with palm of hand or pulp of fingers.
This “just ‘’ touch no pressure contact should be
maintained throughout the stroke.
The hands should work in alternate motions, so that there
is no loss of contact with patients Skin.
At a time only one hand should slide over the pt’s skin.
The stroke should end with a smooth lift of hand.
Slower strokes (12-15/min) are more sedative.
Faster strokes (30-40/min.) are stimulating in nature. PHYSIOLOGIC EFFECT
Soothing & sedative
Stimulates cutaneous touch receptors.
Indirectly improves circulation by activating the axon
reflex.
Facilitates contraction of muscles. effects. THERAPEUTIC EFFECT.
Reduces anxiety, tension & psychological stress.
Decrees hyper sensitivity
Fast stroking elicits contraction in hypotonic
muscles. *Deep stroking / Effleurage
It is the movement of the palmar aspect of hand over the external
surface of the body With constant moderate pressure, in the
direction of venous and lymphatic drainage.
Each stroke begins from the distal end of the segment and is
completed at the proximal end usually at the site of a group of
lymph nodes.
Direction of movement of hand is always from distal to proximal.
Contact and Continuity must be even throughout the stroke.
Depending on area, one or both hands may be used. Pressure is applied by transfer of body weight to the
subject skin through the upper extremity of therapist.
Return stoke is usually superficial.
Rate of stroking is usually slow (10-12/min) to allow
refilling of venous & lymphatic Channels.
In babies with “C” grasp effleurage is done from
proximal to distal. Therapeutic uses
Removal of edema.
Removal of metabolites & inflammatory
products.
Pressure Manipulation
Kneading
• Palmar, Digital, Ironing.
Petrissage
•Picking-Up, Wringing, and Skin rolling.
Friction
Circular, Transverse
Kneading
It is a pressure manipulation
It is a technique in which tissues is pressed down on to the
underlying structures.
Pressure is applied in a circular way along the long axis of
underlying bone.
The Pressure is Increase and Decrease in gradual manners.
Hands are placed over the skin and tissues are
compressed against the bone and hands are moved in a
circular direction.
Several small concentric circles are performed to the body surface
and each circle overlaps the previous one.
½ the circle Pr. is Increase and ½ it is Decrease.
Thus each circle has 2 phases.
(i) Phase of compression
(ii) Phase of relaxation
Increase Pr. should always be proximal to distal.
Kneading can be applied with part of fingers, thumb or palm of
one or both hands.
Palmar Kneading
Performed with whole of palmar or with heel of hand.
Usually performed over larger areas such as thigh, calf, arm etc.
Both the palms are placed on opposite aspects of limb segment (medial and
lateral)
Fingers & thumb not in a contact with the skin.
Both hands should perform co-ordinate circular movement, in opposite
directions.
½ Cycle pr Increase and ½ cycle it decreases.
Slow rates of kneading allow deeper penetration.
Digital Kneading (Finger / Thumb)
Finger kneading
palmar aspect of whole finger or part of it may be used.
Whole finger kneading, finger pad kneading & fingertip kneading
can be used.
One finger or 2-3 fingers may be used. To increase contact area.
Thumb & little finger should have no contact the skin.
Thumb Kneading
The tip of one or both the thumbs are used depending on the
side of area .
One thumb may be placed over the other to reinforce the
movement.
Thumb pad and thumb tip kneading techniques are used.
Thumb pad – smaller muscular areas such as thenar eminence.
Thumb tip- Narrow area such as interosseous spaces.
Reinforced kneading / Ironing
Utilizes both the hands for kneading
Used when greater depth is required.,
Most commonly used over back.
Hands placed over each other on the skin.
Elbow of therapist in extension.
Intermittent circular Pr. is transmitted to the body.
Petrissage or working
Derived form French word “Petrir’’ meaning to “knead’’.
The direction of application of Pr. differentiates petrissage from
Kneading
Kneading exerts vertical compression of soft tissues over underlying
bone and petrissage involves picking up movement of soft tissue with a
lateral compression.
Intermittent Pr. is applied at right angles to the long axis of bone.
Picking up, skin rolling & wringing are the petrissage techniques.
Picking Up
Involves lifting of the tissue up at right angles to the
underlying bone, squeezing and Releasing it.
The web space between thumb and index finger lies across
the central line of the muscle bulk and skin to be lifted.
The thumb and thenar eminence are placed on one side and
index, middle finger placed over the other side of the central
line.
Transfer of body weight to skin through upper extremity to apply compressions
initiates the technique.
Same time grasp of hand is tightened along with little extension of wrist.
Skin Rolling
Involves lifting and stretching of the skin between the thumb and the fingers as
well as moving the skin over the subcutaneous tissue.
Therapist lifts up and moves the skin and superficial fascia with both the hands
keeping a roll of the skin raised continuously ahead of the moving thumb.
Thumb is abducted in such a way that the tip of thumb and index fingers of both
hands touch each other maintaining a full palmar contact with the skin.
Pull the finger backwards with sufficient pressure so that skin is pulled up.
At the same time thumb is adducted and opposed with downward pressure over
the underlying skin.
The coordinated motion of thumb and fingers lifts off a roll of skin from
the underlying structures.
Palm is gradually lifted off the skin so that lifted roll of skin remains
between tip of fingers and thumb.
Move the thumb forward to roll the lifted skin against the fingers.
Main effect of this technique is to stretch the cutaneous and subcutaneous
tissue and induce relaxation.
Usually performed over the back.
Skin Rolling.
Muscle Rolling
Applied over arm, calf thigh muscles.
Whole muscle is lifted between the tip of thumb and fingers,
using similar grasp
Alternately apply and release pressures with thumb and fingers
which rolls muscle fibers from side to side.
Wringing
Grasp and placement of hand similar to picking up.
Both hands are used in opposite aspects of the limb.
Lifting up the skin is done and both hands move in opposite
directions.(Forward & backward)
Useful for mobilization of adherent skin.
Physiologic & Therapeutic uses
(Kneading & petrissage)
Mainly break down of adhesions.
Reduce edema.
Increase mobility of adherent structures.
Friction or Rubbing
It consists of small range oscillatory movement which is applied
to the deeper structures Pressure by thumb or fingers.
According to direction of movement it grouped as.
(i) Circular Friction
(ii)Transverse friction.
Circular friction
Advocated by wood in1974. Resembles digital kneading.
Only difference is continuous Pressure is applied during whole
procedure no phase of Relaxation.
Movement in circular direction. Increase Pressure when superficial
Structures become relaxed.
Applied around localized area (joints, muscle attachments fibrocytic
nodules.)
Used in case when nerve trunk is imbedded in consolidated edema
fluid. Localized effects on muscles are in prolonged state of tension.
Transverse friction
Movement is transverse (i.e.) across the long axis of the structure to be
treated.
Performed with tip of the thumb, index or middle finger, which can be
reinforced, 2 or 3 fingers.
Ligaments to be treated should be in taut position.
Muscles to be treated should be in relaxed position.
It is a painful procedure and patient is to be informed about it priorly.
Physiologic and therapeutic effects
❖ Breaks down intra-fibrillary adhesions.
❖ Smoothens the rough gliding surfaces.
❖ Ensures pain free mobility.
❖ Useful in traumatic muscular lesions, tendonitis, tenosynovitis and
ligament sprain.
❖ Much useful in localized pain (trigger points).
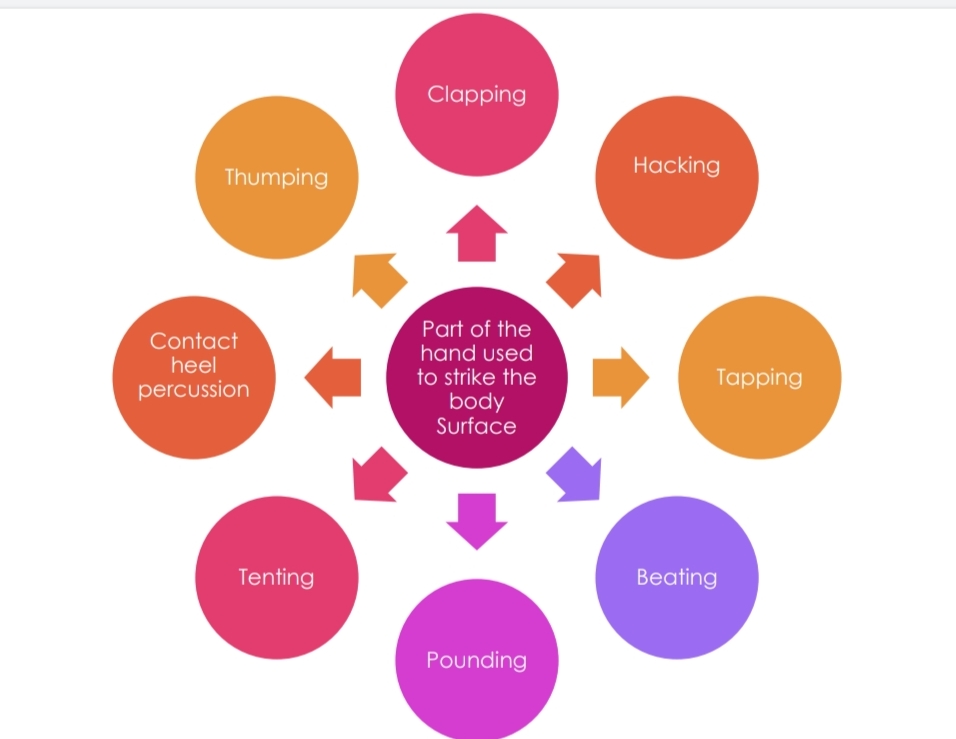
Percussion or Tapotement
French word which means striking of two objects against each
other.
Utilizes controlled movement of wrist and forearm to strike the
patients body surface Rhythmically.
Mild blows are applied with various pressure and in different
manners.
Clapping or Slapping
Used in management of chronic respiratory disorders which
leads to sputum retention
Slightly cupped hands strike the chest wall alternately in
predetermined rate.
Fingers and thumb are adducted and M.P. joints of fingers are
slightly flexed in position.
Palm should not come in contact with patient’s body during
striking.
No movement at elbow, only wrist flexion and extension should be
done rapidly.
Hand should create air cushion between the hand and the chest
wall on impact.
Performed during both inspiration and expiration.
Manual percussion normally 100 – 480 times / Min.
Clapping is performed over chest wall, with a blanket or towel
covering it.
Clapping or Slapping.
Hacking
The ulnar border of medial 3 fingers is used to strike the skin.
This produces a peculiar sound
Alternate supination and pronation of forearm combined with
radial deviation of the wrist respectively produce hacking.
Applied over larger areas such as back and thigh etc.
Tapping
Useful when intermittent touch and pressures are to be applied over a
small area.
Only the pulp of fingers strikes the body part.
One of both hands may be used.
Alternate flexion and extension of the MCP joints produce the tapping.
No movement should be at wrist and elbow.
Commonly used over face, neck and other smaller areas.
Conveniently used on children.
Beating
Anterior aspect of the clenched fist strikes the body part.
In making fist, fingers are flexed at MCP and PIP joints but DIP is
kept extended to produce a flat surface, which is used for beating
Beating is produced by alternate flexion and extension of wrist.
No movement at elbow.
Used over back, thigh and other fleshy and broad area of body.
Pounding
Fingers are flexed at all the joints to make a fist.
Thumb rests over the index finger.
Supination and pronation of forearm combined.
Ulnar and radial deviation of wrist respectively produces the pounding
Used over back, thigh and other fleshy and broad areas of the body.
Ulnar border of clenched fist strikes the body.
Tenting
It is a modification of clapping.
Here concavity is produced between the index and the ring finger with the
middle finger slightly elevated and placed over them.
For loosening secretions in the smaller chest of newborn or a premature infant.
Contact Heel percussion
It is a modification of clapping.
Concavity is produced between thenar and hypothenar
eminences.
Thumping
Apply pressure over the body surface with dorsal aspect of clenched fist.
Usually applied over back and chest.
Helps in increase exhalation.
Helps in coughing up material from bronchial emphysema.
Vibration
Involves constant touch of therapist hand and application of rapid intermittent
pressure with out changing the position of hand.
Usually used over chest wall.
Can be produced by one fingertip or palm.
The therapist should produce isometric contraction of all the muscles of upper
extremity which are transmitted to the patient’s body surface through his hands.
This produces oscillatory movements of his hand in upward and downward
direction and
Transmits the mechanical energy to the patient’s chest.
Shaking
Oscillation is coarse compared to vibration.
Fore arm in midprone position.
Oscillation occurs in side ways movement
Patients in supine lying, Place both hands on each side of anterior Chest
wall or antero posteriorly on same side.
Patient’s in side lying , place both hands on the upper lateral chest wall
or antero posteriorly on the upper side chest wall .
Shaking is done during expiratory phase.
Therapist tends to produce upward and down ward movement of upper extremity.
This shakes chest wall vigorously .
While shaking is done for extremities , they should be raised to encourage venous
and lymphatic return .

Doing great 👍👍
LikeLike
Well done doing great work 👍
LikeLike